After the Bondi Attack, Scrutiny Turns to the Philippines—But the Real Threat is Global
Reports linked the Bondi attackers to training in the Philippines, but evidence is scant. This analysis explores the reality of Islamic State factions in Mindanao and the broader threat of a resurgent global insurgency.
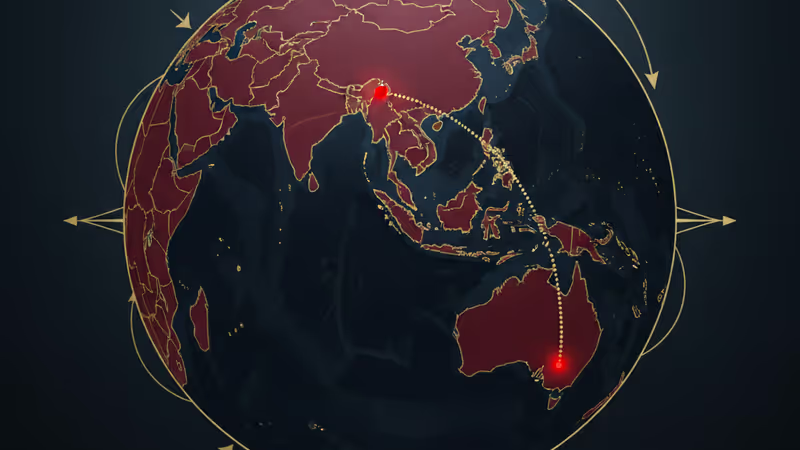
The finger of blame for Australia's worst mass-casualty terrorist attack quickly pointed to the Philippines, amid reports the Bondi shooters received training there. However, the evidence for a direct link is tenuous at best, and the incident reveals a more complex picture involving the fragile Bangsamoro peace process and the reconstitution of the Islamic State as a global threat.
Conflicting Narratives: IS Praise and a Filipino Rebuttal
Soon after the December 14 attack, Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese indicated the perpetrators were inspired by the Islamic State. Then, on December 18, IS's Al-Naba magazine praised the father-son duo as the 'Pride of Sydney' in its issue 526. Yet, the group stopped short of claiming responsibility, instead emphasizing its strategy of inciting lone-actor attacks, which don't require formal connections to the organization.
The Philippines government pushed back forcefully. National Security Adviser Eduardo Ano asserted that describing Mindanao as a terrorist breeding ground is 'outdated and misleading,' calling for evidence-based reporting. This reflects Manila's frustration that its significant counter-terrorism efforts are being overlooked.
The Reality in Mindanao: A Weakened, Insular IS Presence
The southern island of Mindanao has a 50-year history of cyclical violence and peace negotiations. The most recent push led to the formation of the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM) in 2019, ushering in a promising period of stability. However, local IS-aligned groups are committed to collapsing this peace process.
However, a Guggenheim-funded study of over 250 former combatants offers crucial insight. It shows that pro-IS groups have been devastated by counter-terrorism operations, particularly since the 2017Marawi Siege. The picture that emerges is of groups that are weak, fragmented, and insular, operating primarily through close family and kinship networks. This very insularity makes it extremely difficult for foreigners to join their ranks.
本内容由AI根据原文进行摘要和分析。我们力求准确,但可能存在错误,建议核实原文。
相关文章
中國官 方智庫學者樊恩實警告,為反制西方主導歷史觀點的「去中國化」威脅,中國應建立一套關於邊疆歷史的原創知識體系,以鞏固國家安全與國際話語權。

孟加拉最大反對黨領袖塔里克・拉赫曼在流亡17年後將返國,預計500萬支持者將集結首都。此舉為明年2月的國會大選投下變數,考驗該國脆弱的民主轉型。

尼泊爾前總理奧利在爭議聲中三度連任CPN-UML黨魁。他因鎮壓Z世代抗議致77死而受查,此番當選不僅違背民意,更可能引發尼泊爾政局的劇烈動盪。

馬來西亞政府在泰國對澳洲記者韓特提起跨國誹謗訴訟。本文深入分析「惡意訴訟」(SLAPP)如何成為跨國鎮壓工具,及其對東南亞言論自由構成的嚴重威脅。